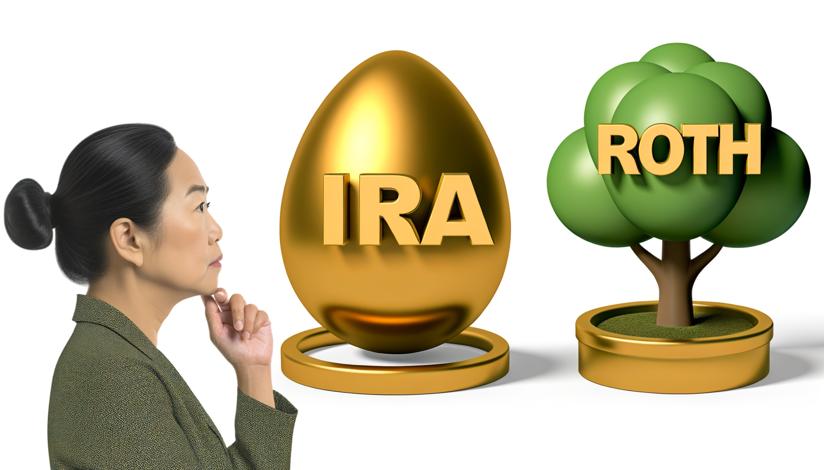
A traditional IRA is a tax-deferred retirement account. Contributions to a traditional IRA are made with pre-tax dollars, meaning you don't pay income taxes on the money you contribute. Instead, you pay taxes on your withdrawals in retirement. This can be advantageous if you expect your income to be lower in retirement, as you may pay a lower tax rate on your withdrawals.
On the other hand, a Roth IRA is a post-tax retirement account. Contributions to a Roth IRA are made with after-tax dollars, so you won't receive a tax deduction for your contributions. However, qualified withdrawals from a Roth IRA are tax-free. This can be beneficial if you anticipate being in a higher tax bracket in retirement or if you want to leave a tax-free inheritance to your beneficiaries.
One key difference between the two types of IRAs is the age at which you must start taking required minimum distributions (RMDs). With a traditional IRA, you must start taking RMDs at age 72, whereas with a Roth IRA, there are no RMDs during your lifetime. This can give you more flexibility in managing your retirement withdrawals and may allow you to leave more money in your account for a longer period of time.
Another factor to consider is eligibility. Anyone with earned income can contribute to a traditional IRA, regardless of age. However, there are income limits for contributing to a Roth IRA. In 2021, you can contribute the full amount to a Roth IRA if your modified adjusted gross income (MAGI) is less than $125,000 for single filers or $198,000 for married couples filing jointly. The amount you can contribute phases out as your income approaches the upper limits.
If you have a 401(k) through your employer, you may also want to consider whether a traditional IRA or a Roth IRA is a better complement to your 401(k) savings. Traditional IRAs and 401(k)s have similar tax treatment, as contributions to both are made with pre-tax dollars. Roth IRAs, on the other hand, offer the potential for tax-free withdrawals in retirement. Depending on your income, tax bracket, and other factors, one option may be more advantageous than the other.
For self-employed individuals, there are additional retirement savings options to consider. A traditional IRA or a Roth IRA can still be a good choice, but you may also want to explore self-employed retirement plans such as a Simplified Employee Pension IRA (SEP IRA) or a Solo 401(k). These plans offer higher contribution limits and additional tax advantages for self-employed individuals.
In conclusion, choosing between a traditional IRA and a Roth IRA depends on your unique financial situation and goals. Consider factors such as your tax bracket now versus in retirement, your eligibility for contributing to a Roth IRA, and whether you have a 401(k) through your employer. Additionally, self-employed individuals may want to explore self-employed retirement plans. By carefully evaluating your options and seeking guidance from a financial professional, you can make an informed decision that will help you build a secure retirement nest egg.

Tax benefits in retirement
Flexibility in managing withdrawals
Potential for tax-free withdrawals

Paying taxes on withdrawals in retirement
Income limits for contributing to a Roth IRA
Higher contribution limits for self-employed retirement plans

























-
https://www.irs.gov/retirement-plans/individual-retirement-arrangements-iras
-
https://www.investopedia.com/terms/i/ira.asp
-
https://www.fool.com/investing/2019/12/05/traditional-vs-roth-ira.aspx